What is Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
A hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test reflects the average concentration of glucose (sugar) in blood over the previous 2-3 months. The test measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin (the protein present in red blood cells that carry oxygen) and is reported as a percentage of total hemoglobin. Having a consistently high HbA1c level indicates either type 2 diabetes or a heightened risk for developing diabetes (pre-diabetes).
Why Measure Your Hemoglobin A1c
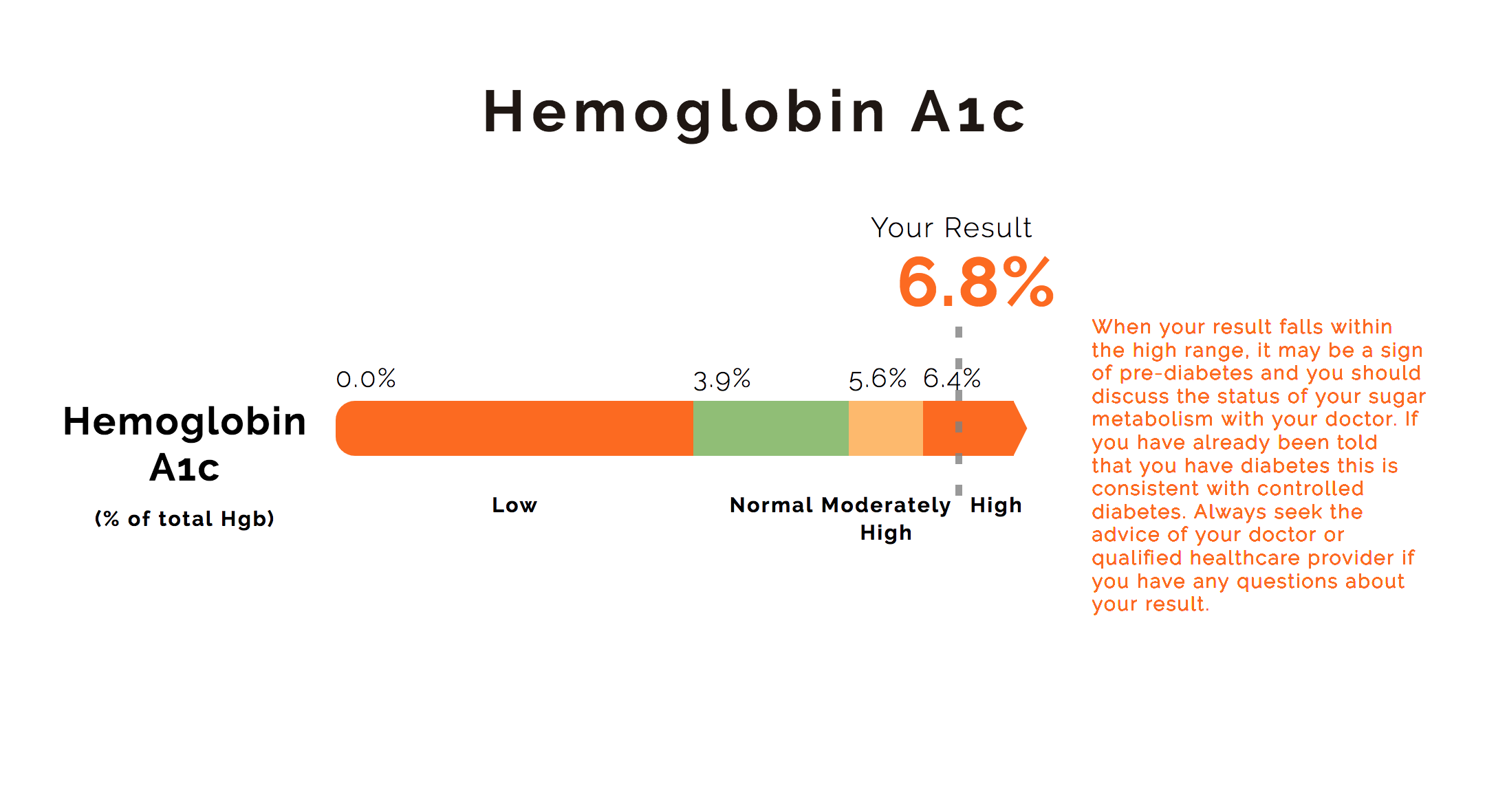
A normal HbA1c level is 5.6% or below while an HbA1c from 5.7% to 6.5% is indicative of pre-diabetes. Without lifestyle intervention, 15%-30% of individuals with pre-diabetes are likely to develop type 2 diabetes within 5-10 years. If you receive an HbA1c screening result in the pre-diabetes range, contact your physician so that he or she can work with you to reduce your risk for type 2 diabetes.
An HbA1c result of 6.5% or greater indicates type 2 diabetes. If you receive an HbA1c screening result of 6.5% or greater, contact your physician right away so that he or she can work with you to manage your condition.
Screening for HbA1c is a best practice, and the following exemplifies why. When looking at the Quest Diagnostics $1-per screening campaign with the American Diabetes Association,® Quest came across something shocking. Of those screened during the campaign 35% had a normal glucose result but an elevated HbA1c, putting them in the pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes range. If this program measured glucose only, 35% of those with a normal glucose may not have known of their condition. Including an HbA1c test in your wellness screening may be key to understanding your risk of diabetes.