What is Glucose?
Glucose is the chief source of energy for your body, and is often called “blood sugar.” A glucose test measures the concentration of glucose in your blood at the time of the test, and is used to ensure that your body is breaking down sugars correctly after eating, and you aren’t at risk for type 2 diabetes. Having a consistently out-of-range glucose level indicates a heightened risk for diabetes and other health problems such as hyperthyroidism or liver disease.
How to Measure Your Glucose Level
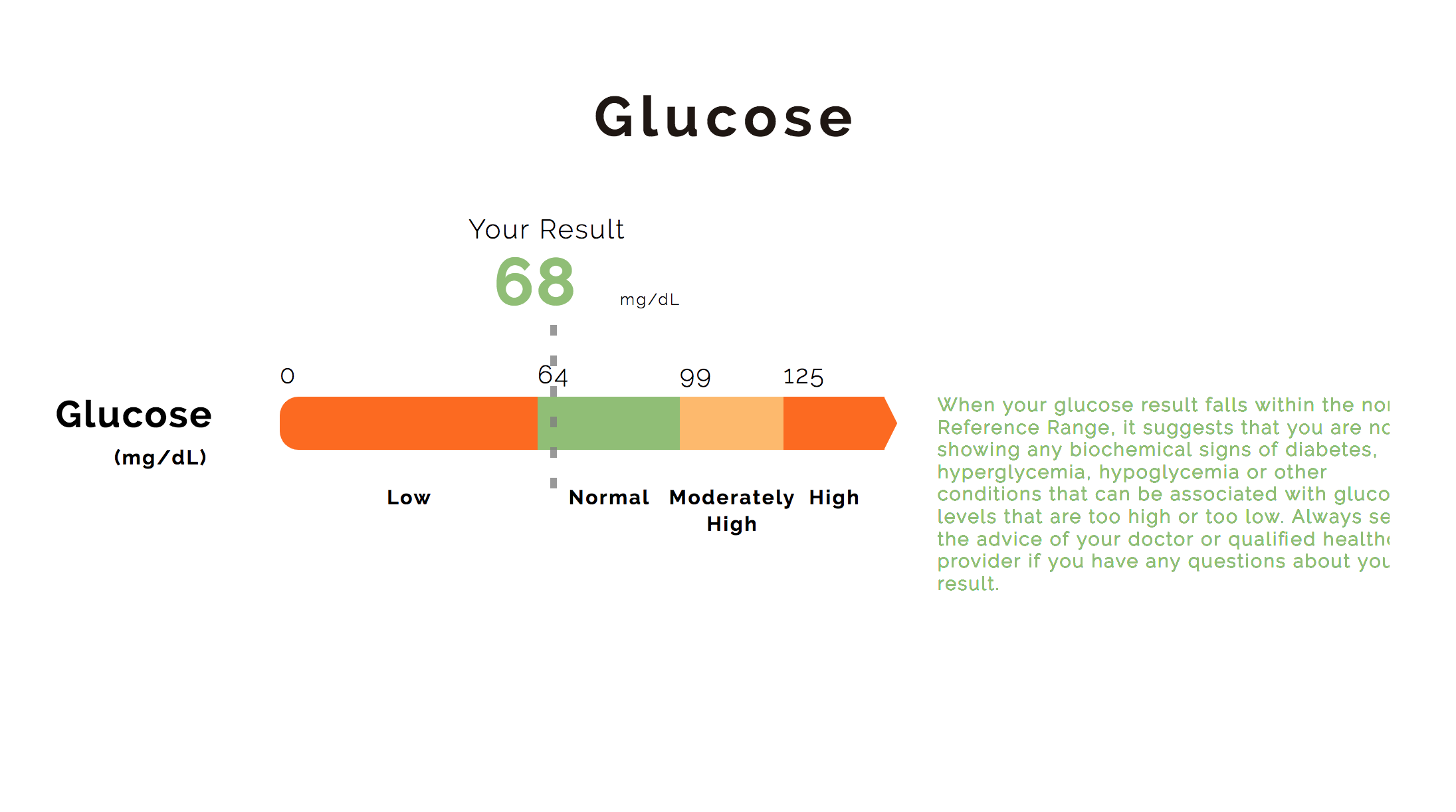
Since a glucose result reflects what you’ve recently eaten, whether or not you have eaten prior to your screening impacts your result. Quest Diagnostics Health & Wellness has different reference ranges based on whether or not you have fasted prior to your screening.*
If you have fasted for 9-12 hours prior to your screening, a normal glucose level is between 65 and 99 mg/dL. If you have not fasted for 9-12 hours prior to your screening, a normal glucose level is between 65 and 140 mg/dL. If your result is below the normal range, it is referred to as hypoglycemia, meaning you may have an increased risk of hyperthyroidism or liver disease. If your result is above the normal range, it is referred to as hyperglycemia. This can mean that your body is not correctly using or producing insulin, the hormone that enables your body to utilize glucose. A high glucose result suggests you may have diabetes or pre-diabetes, a condition in which blood glucose is higher than normal but not high enough to receive a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
Good fasting glucose levels can sometimes be misleading
Fasting glucose is measured almost anytime you have blood drawn. Proper blood sugar management is really important, but fasting blood glucose levels aren’t a great indictor of one’s ability to manage blood sugar. It’s a decent first step, but other related testing provides more accurate indication of blood sugar management.
Fasting blood sugar levels can change dramatically, within hours. Most people, even those with insulin resistance, show relatively normal blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tells a more powerful story of blood sugar regulation.
If you receive an out-of-range glucose result, visit your primary care physician to discuss your results and, if needed, to form a treatment plan.
*Fasting blood test means not eating or drinking anything but water for 9-12 hours prior to your screening.